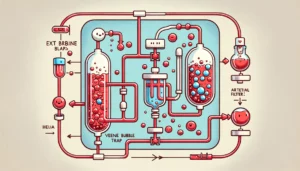
Increased White Blood Cell Count is Associated with an Increased Demand for Unfractionated Heparin During Veno-Arterial Extracorporeal Oxygenation in Lung Transplantation
This retrospective study investigated whether increased white blood cell (WBC) counts correlate with higher unfractionated heparin (UFH) dosage needs during veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (V-A ECMO) in lung transplantation. Among 27 patients, those with elevated WBC counts (above 10.2 × 10³/μL) required higher UFH doses to maintain targeted clotting times. The findings suggest WBC count could help determine optimal UFH dosing during surgery.